
Introduction to Hacking Thick Clients: Part 1 – the GUI
Introduction to Hacking Thick Clients is a series of blog posts that will outline many of the tools and methodologies used when performing thick client security assessments. In conjunction with these posts, NetSPI has released two vulnerable thick clients: BetaFast, a premier Betamax movie rental service, and Beta Bank, a premier finance application for the elite. Many examples in this series will be taken directly from these applications, which can be downloaded from the BetaFast GitHub repo. A brief overview is covered in a previous blog post.
Installments:
Overview
The thick clients we come across most often at NetSPI are written in C# and a bit long in the tooth. In these applications, there are two main GUI platforms: Windows Forms and Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF).
Windows Forms
Windows Forms was state of the art in 2002. And it’s not half bad in 2020! Basically, a form is composed of controls, which are your typical Windows objects such as text boxes, labels, buttons, etc. And each of these objects has its own properties, methods, and events.
Consider the following Windows Forms login form:
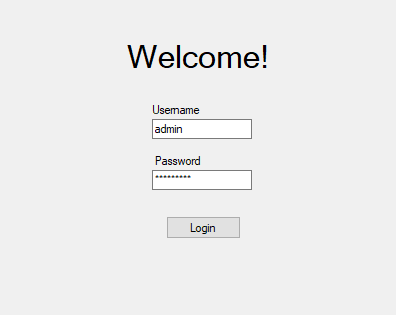
An administrator’s credentials are saved. Nice! Let’s steal those for later!
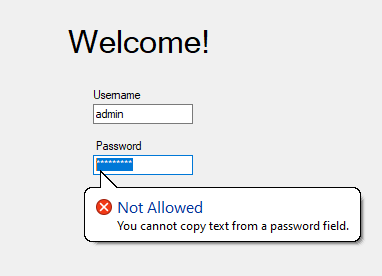
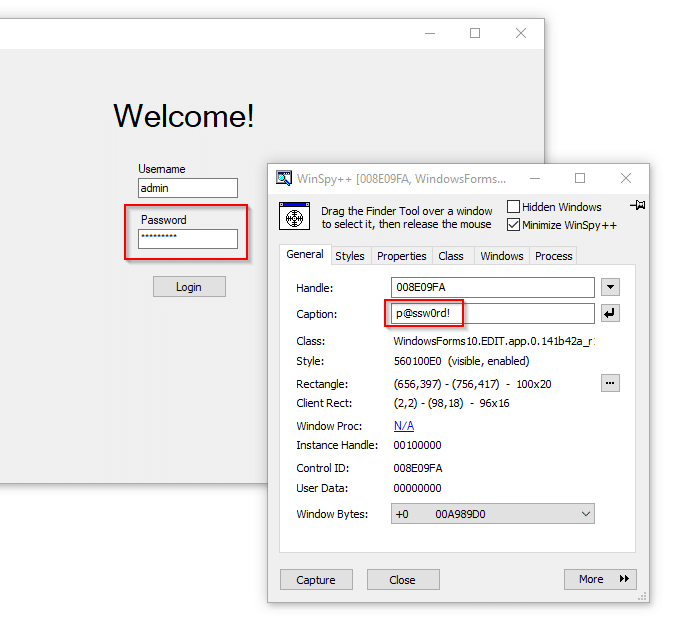
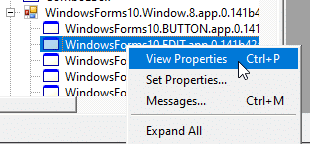
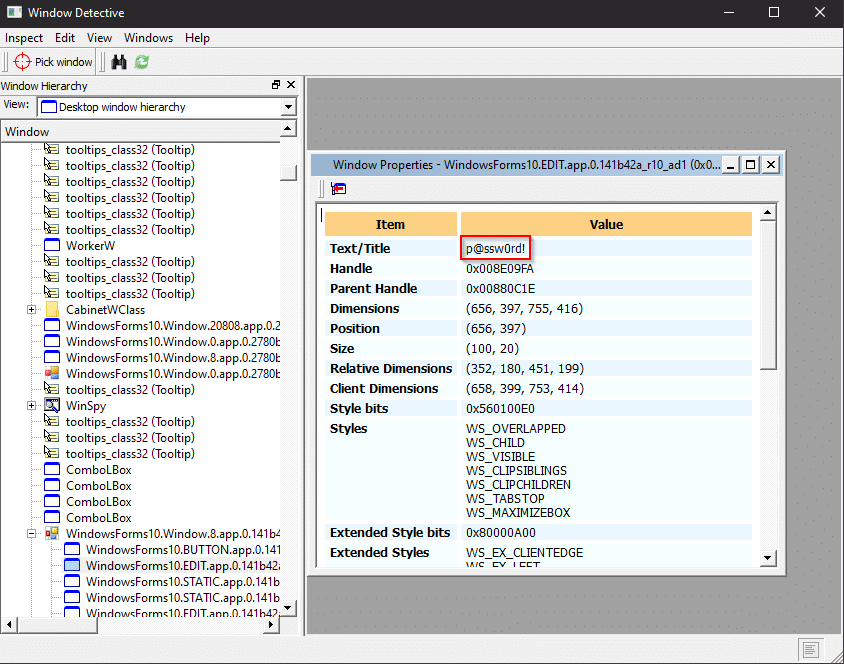
Darn! Thankfully, there are some tools at our disposal that allow us to view and modify controls. The first is WinSpy. Simply target a control and note that the masked value is stored in plain text.
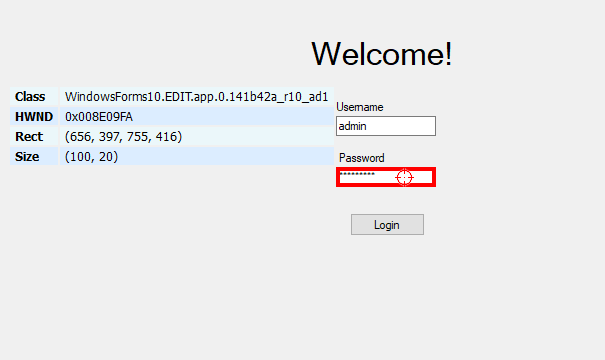
Another similar tool for targeting Windows Forms objects is Window Detective. Selecting a control will highlight the object in the desktop window hierarchy. There, you can view its properties, including the elusive password.
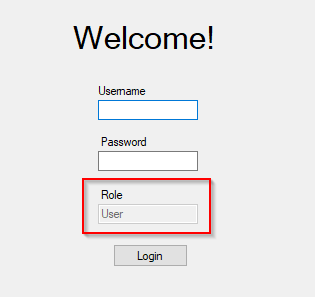
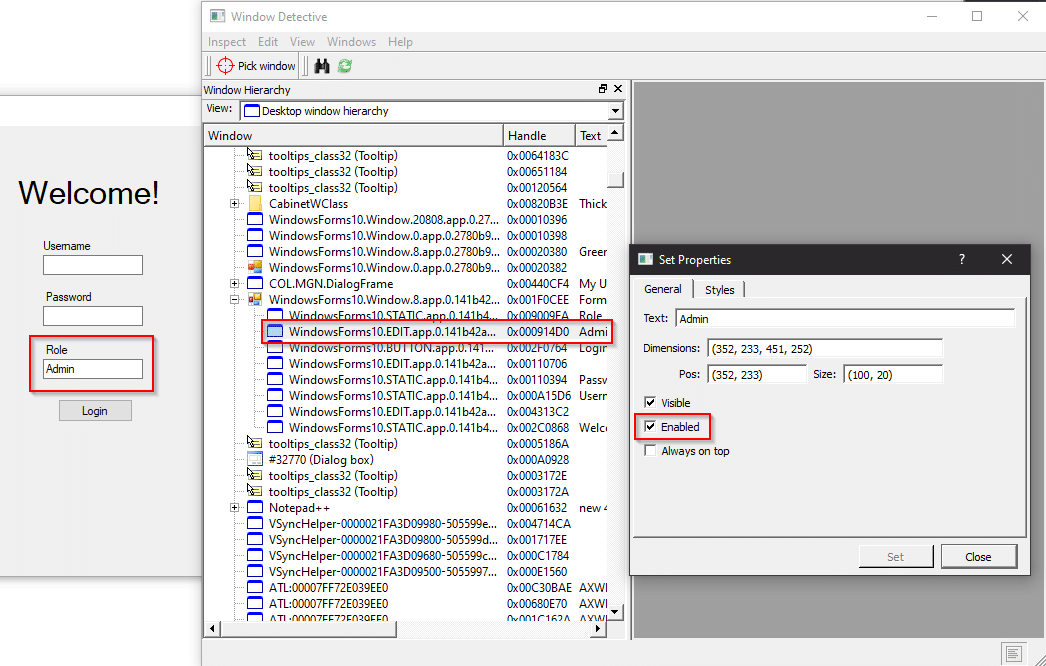
Here’s another Windows Forms example. This application verifies the Role on the client-side and has the text box disabled so it cannot be changed.
But with WinSpy and Window Detective, we can set the text property to Admin.
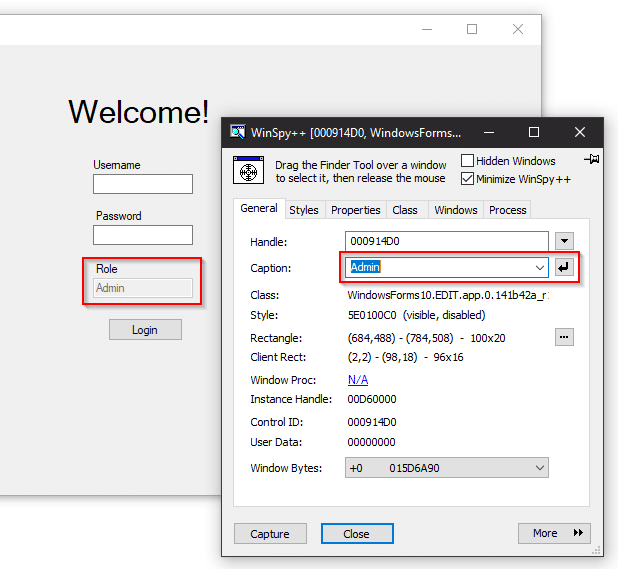
And why not just change the Enabled property to true?
Some applications attempt to ward off SQL injections or other attacks by limiting the length of input or the types of input characters. But relying on any client-side control is a clear security risk.
Windows Presentation Foundation
WPF was released a day before Tenacious D in The Pick of Destiny and has aged just as well. It’s more complicated to work with than Windows Forms, but allows for a much more customizable design. A WPF-focused tool such as Snoop is needed for this platform.
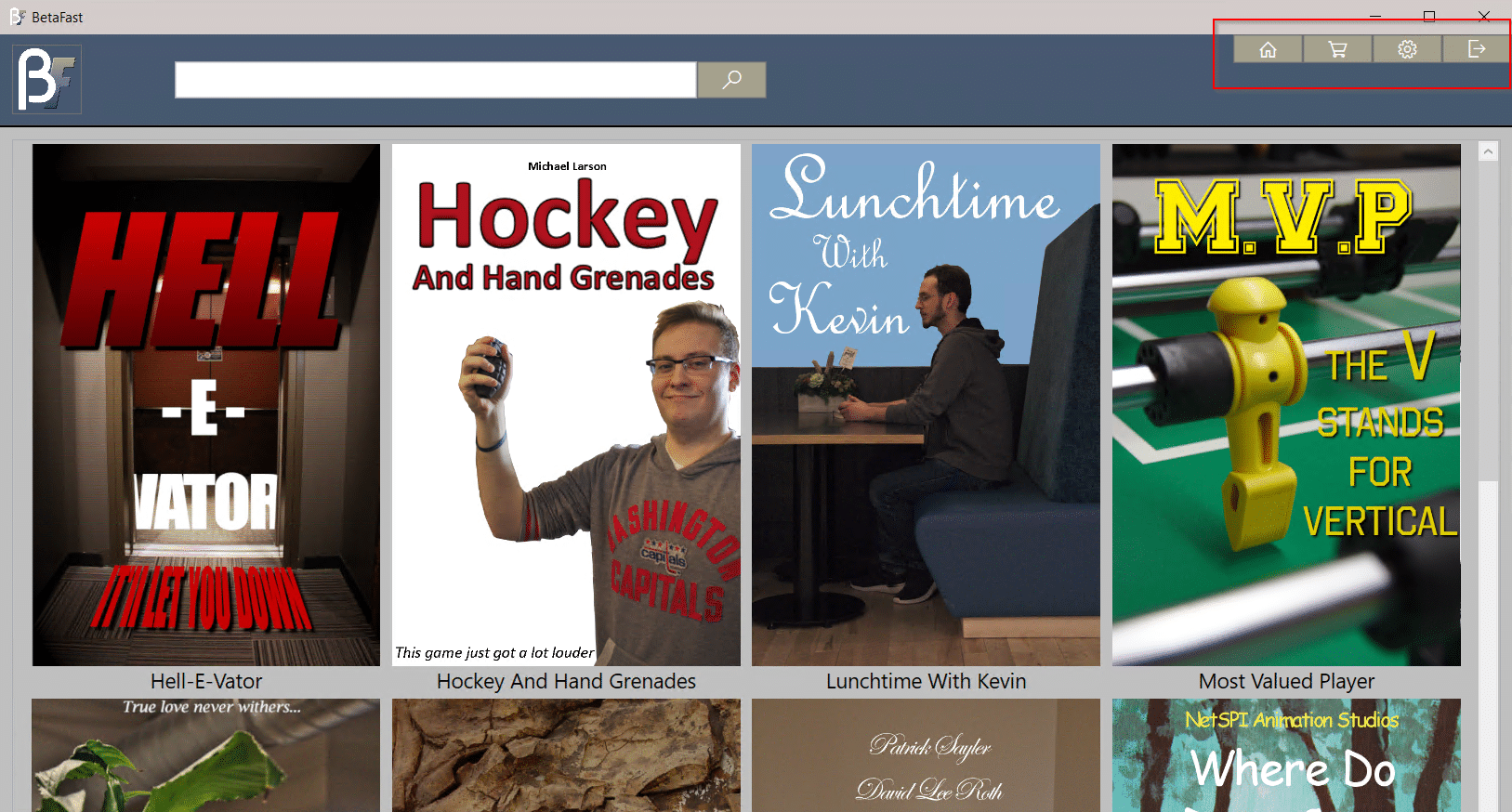
Authenticate to BetaFast as a typical user and note that there are four menu items: Home, Shopping Cart, Settings, Logout.
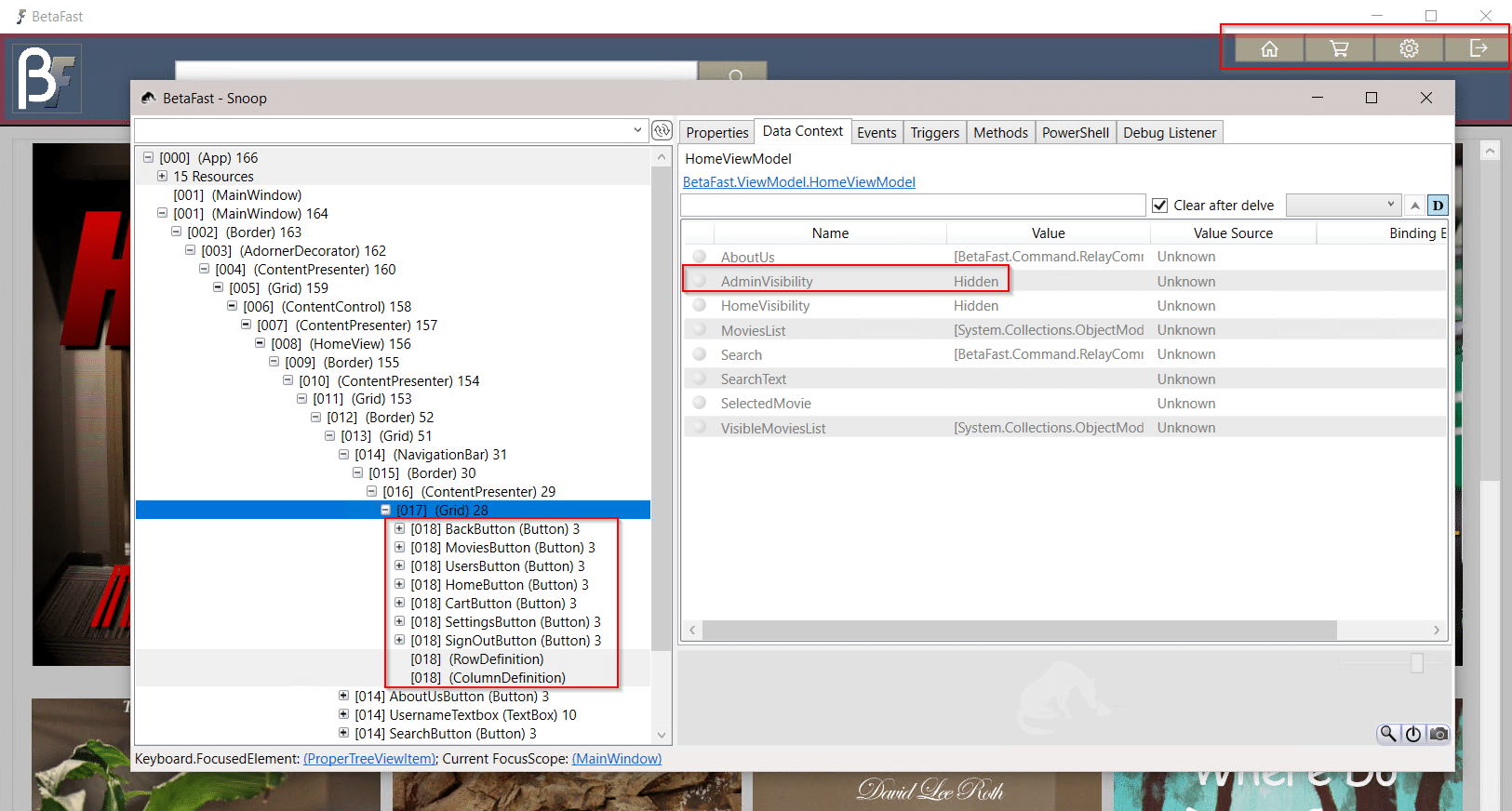
By connecting Snoop to the application process, the design tree can be expanded to reveal an AdminVisibility property set to Hidden.
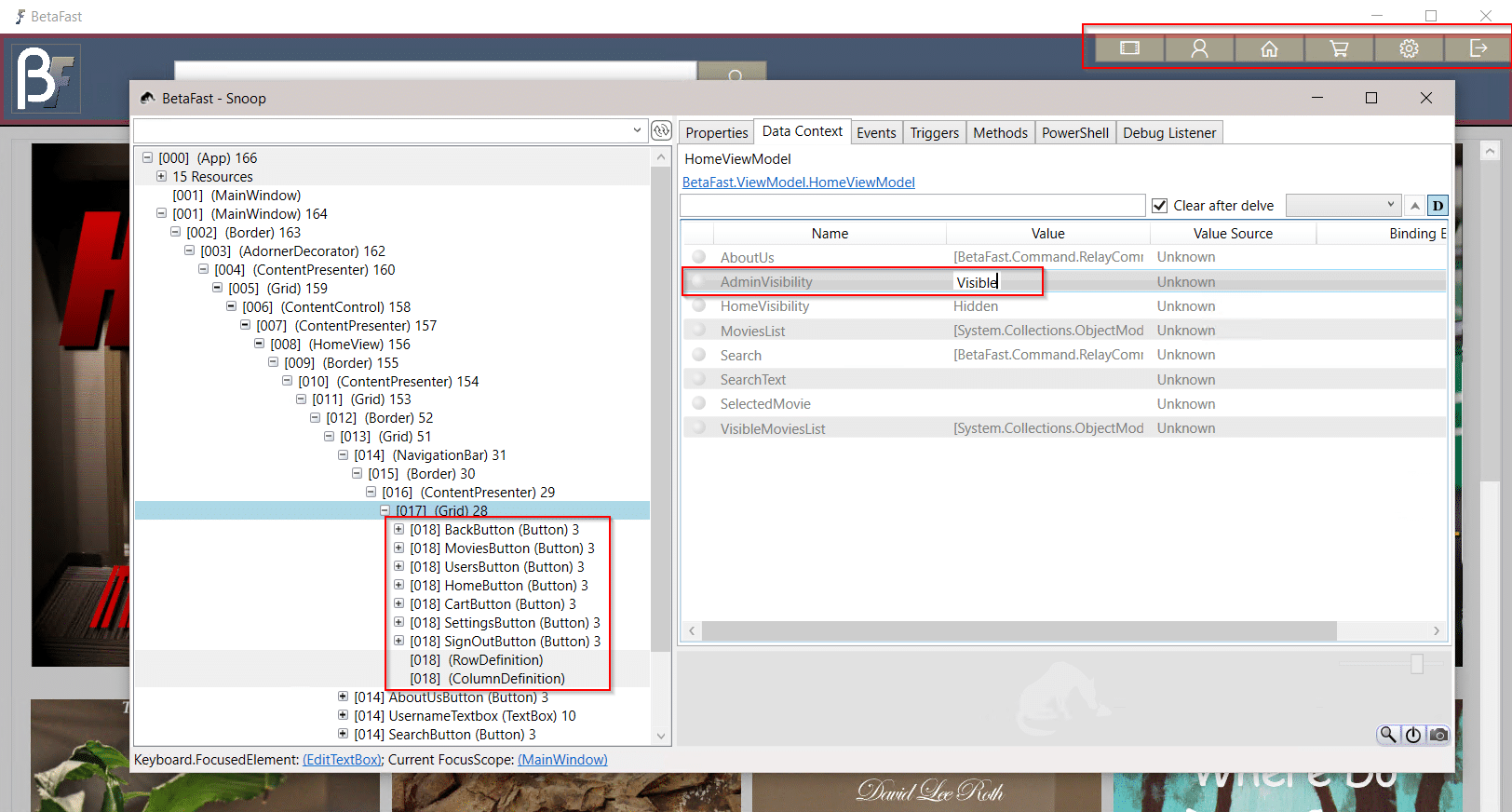
Changing this value to Visible reveals additional menu items restricted to administrators.
By itself, this is not a vulnerability. Any functionality in these restricted pages should have server-side authorization checks. However, this is often not the case. Below, a User is able to create an Admin account and view all of the accounts in the database.
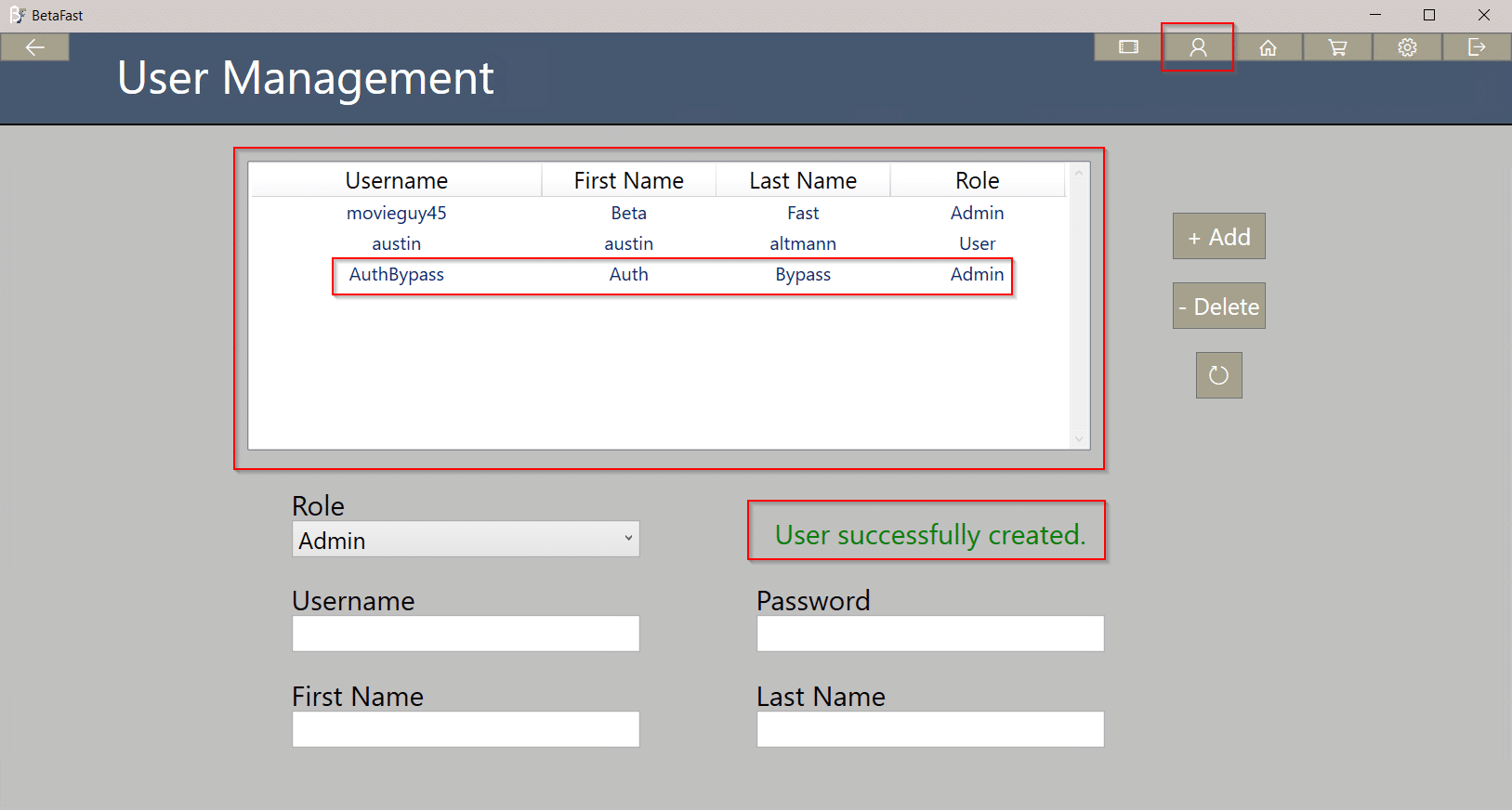
The payment page of this application verifies the total rental cost in the client, not the server.
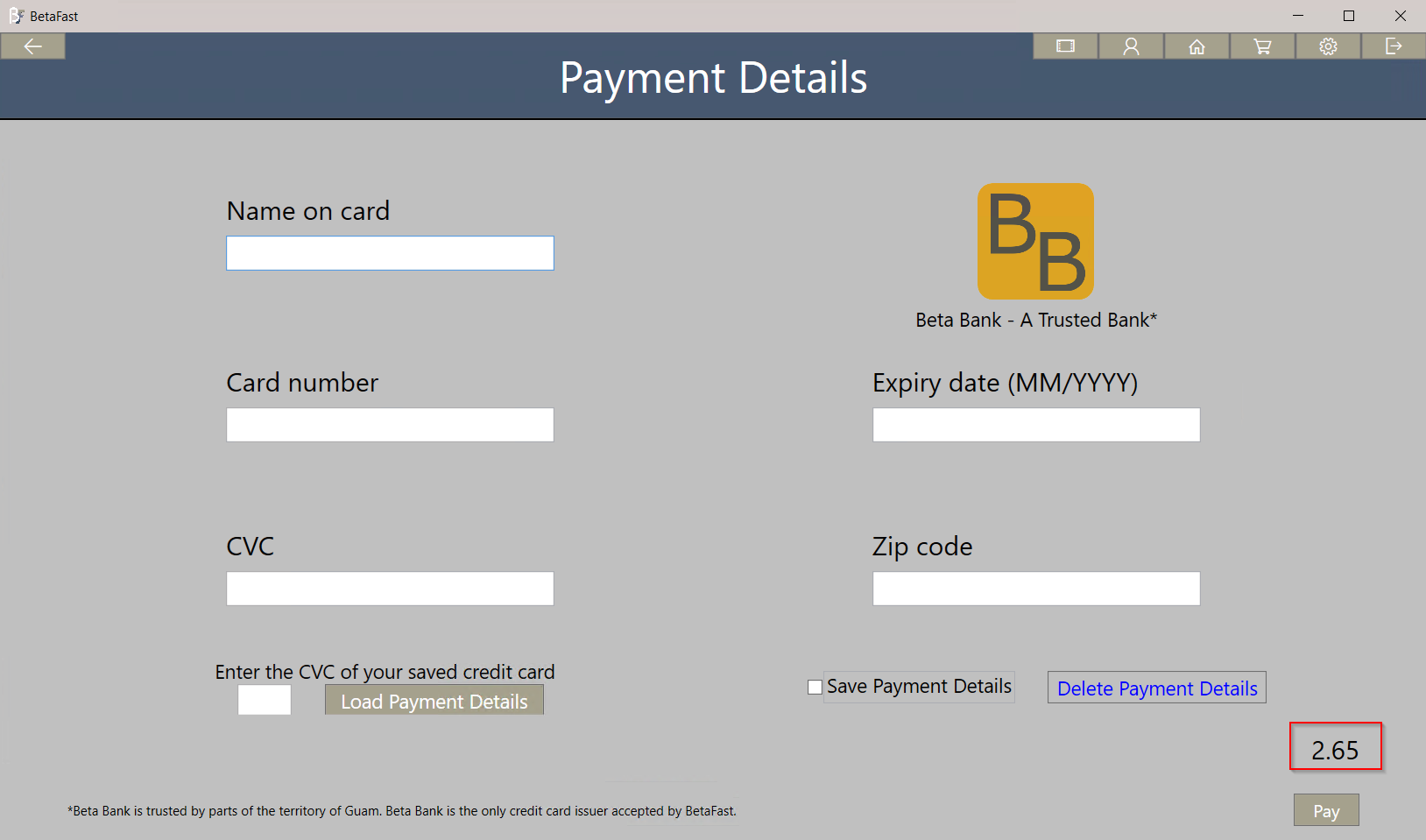
That means we can use Snoop to get a nice discount on these Betamax tapes – perhaps store credit?
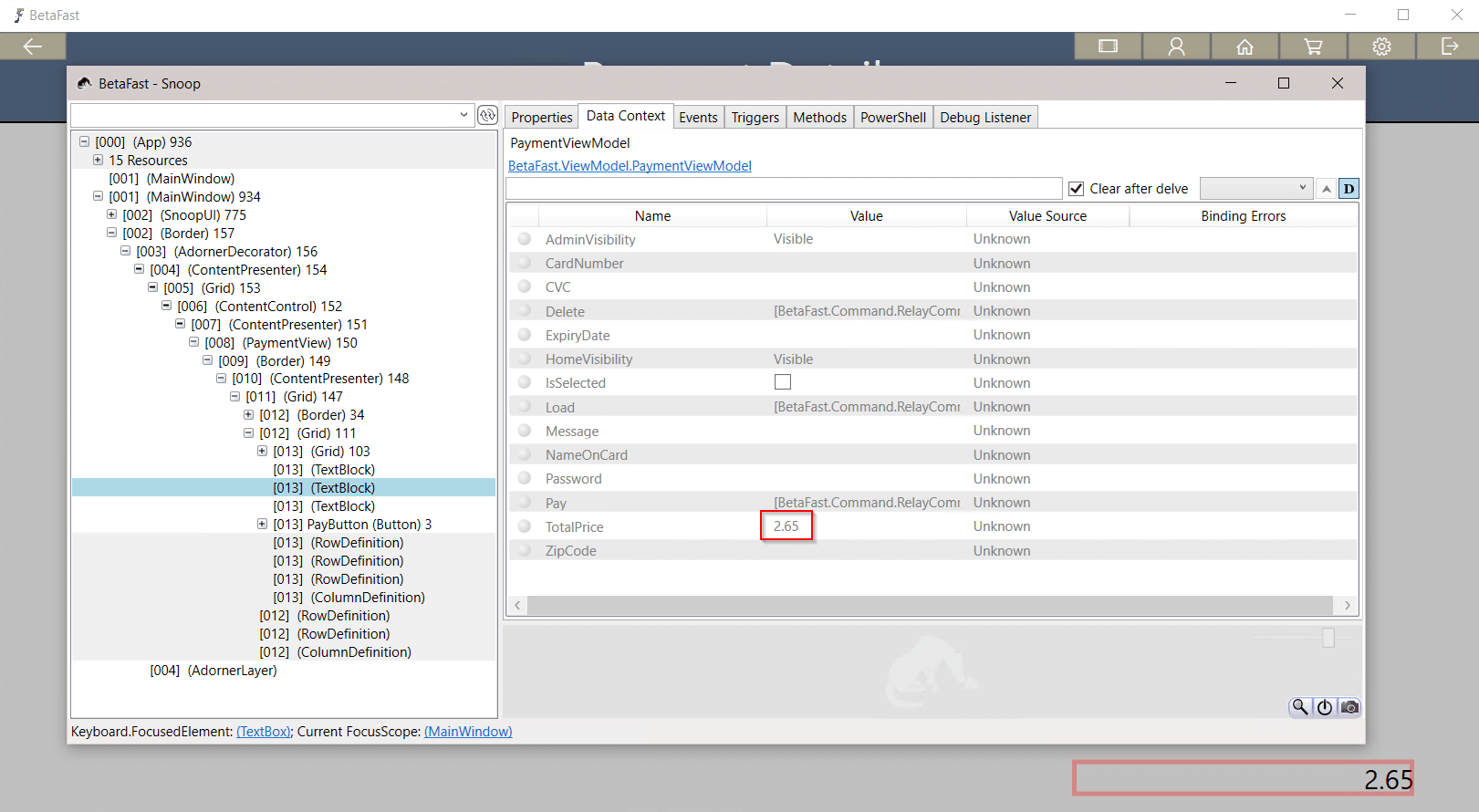
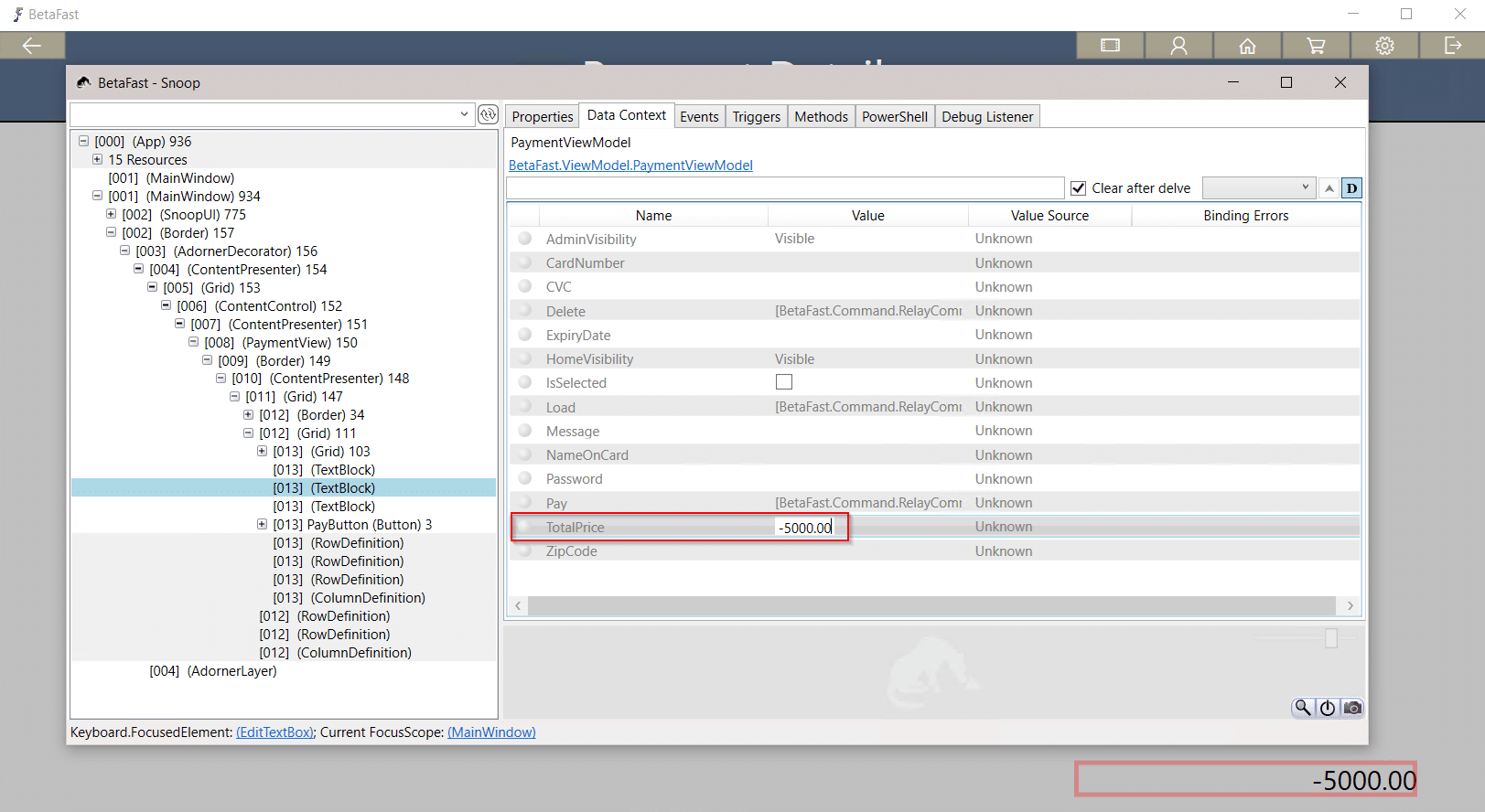
Closing Remarks
Modifying GUI elements in thick clients is rather straightforward, especially with a set of polished tools. The remediation steps for any of these vulnerabilities are simple as well:
- Perform authorization and input validation on the server
- Do not hide sensitive data behind GUI designs
I’ll add another link to our BetaFast GitHub repo here. Be sure to try some of these examples out yourself, and be sure to tune in for our next installment of Introduction to Hacking Thick Clients.
Explore more blog posts
CTEM Defined: The Fundamentals of Continuous Threat Exposure Management
Learn how continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) boosts cybersecurity with proactive strategies to assess, manage, and reduce risks.

Balancing Security and Usability of Large Language Models: An LLM Benchmarking Framework
Explore the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) in critical systems and the balance between security and usability with a new LLM benchmarking framework.

From Informational to Critical: Chaining & Elevating Web Vulnerabilities
Learn about administrative access and Remote Code Execution (RCE) exploitation from a recent Web Application Pentest.