Move from Passive to Proactive with Offensive Security over Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance has become the standard by which organizations remediate the ever-increasing risk of ransomware by providing companies with a failsafe to recoup their losses. However, industry chatter around cyber insurance premiums increased in the last year as the cost of paying for insurance has shifted to outweigh the potential benefit of receiving a payout in the event of a ransomware event. Insurance premiums and deductibles rose to meet the high cost of ransomware attacks, while coverage from insurance plans shrank, putting more responsibility for proactive security measures on companies in order to qualify for coverage in the first place.
As organizations face double-digit increases to their insurance premiums, the current state of cyber insurance has security leaders questioning whether the investment is worth it. Instead of putting their budget toward insurance, companies may be better off spending their dollars on offensive security measures that create a stronger security posture from the start.
4 Stats that Show the Reality of the Cyber Insurance Market
The cost of cyber insurance is rising to meet the increased cost of data breaches. At the same time, threat actors are relentless in their pursuit of sensitive information, putting every company at risk for an attack. Interestingly, most of these attacks occur using common tactics such as social engineering, or exploiting a vulnerability between systems, as opposed to advanced methods of gaining entry.
Insurance carriers are increasingly requiring these offensive security measures to qualify for cyber insurance, or reduce the cost of insurance.
Because of this, companies need to prove they’ve done their due diligence in securing their environment with baseline measures such as multi-factor authentication, infrastructure access management, user identity and role governance, and training staff to recognize phishing attempts. Insurance carriers are increasingly requiring these offensive security measures to qualify for cyber insurance or reduce the cost of insurance.
The stats below help paint a picture of the reality of cyber insurance today.
- 85% of cyber insurance carriers reported premiums increasing year-over-year (Blackberry)
- $4.35 million is the average cost of a data breach in 2022 (IBM Security)
- 3.5 years is the average duration of a cyber insurance claim payout (Cyber Breach Insights)
- 61% is the increase in direct written premiums since 2021 (National Association of Insurance Commissioners)
In short, these stats tell the story of the increasing cost of data breaches paired with companies paying higher prices for cyber insurance.
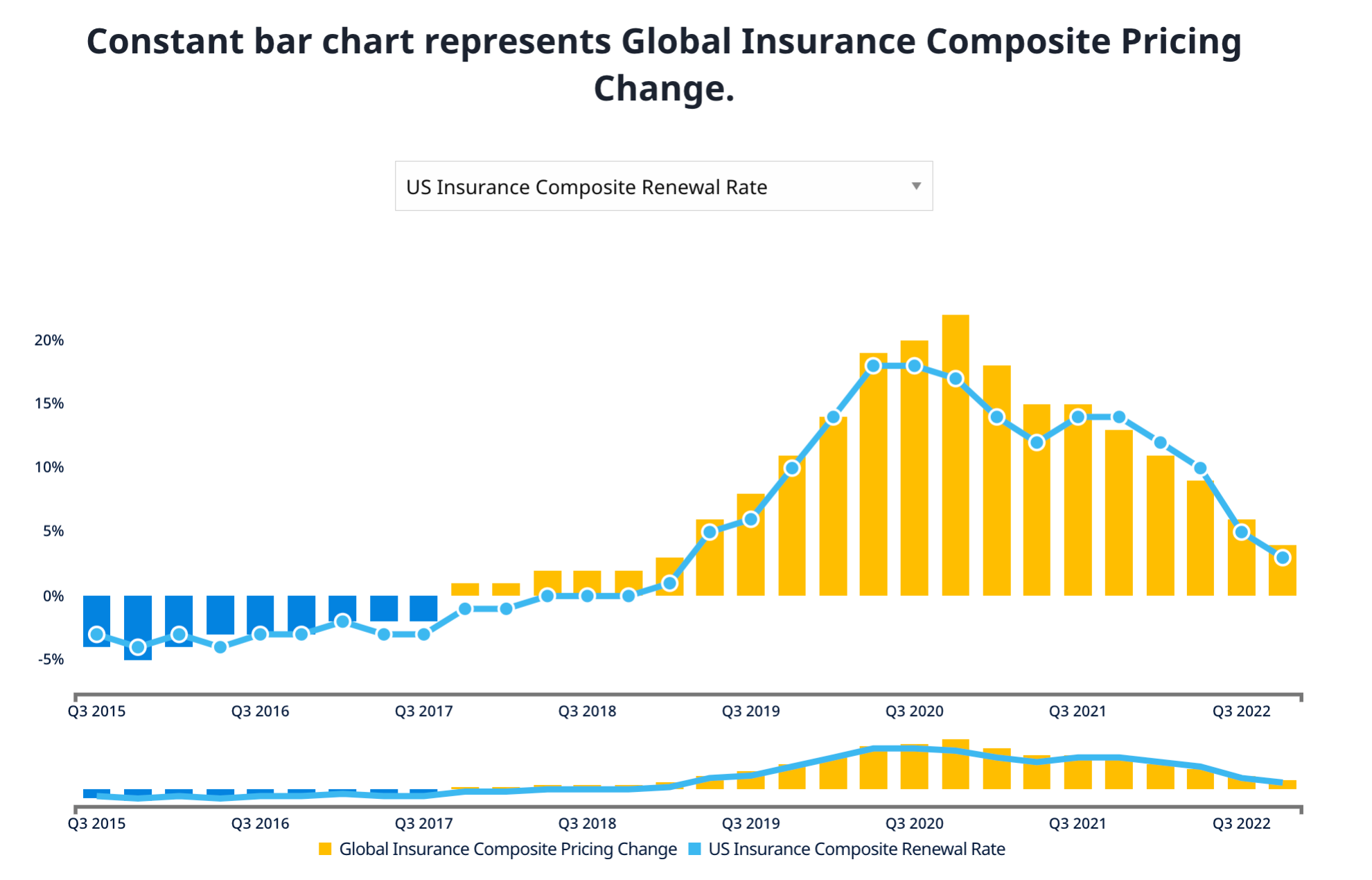
How Much does Cyber Insurance Cost?
The cost of global insurance composite pricing rose sharply starting in Q2 of 2019 and continued a drastic increase through Q4 of 2020. Current data show the market may have stabilized, as composite pricing change is lowering quarter-over-quarter.
The stabilization we’re seeing today doesn’t discount the dramatic increase in costs companies have had to accommodate over the last couple of years. Trends like these may become commonplace as the economy continues to fluctuate.
Cyber insurance is a reactive security measure, meaning companies need to pair it with proactive security steps to establish a bulwark against breaches. Organizations can’t solely rely on cyber insurance as the means of their cybersecurity program. Paying insurance premiums means money spent on coverage may never come back to benefit your organization. However, investing in offensive security results in a compounded return on investment by reducing the potential for ransomware.
Achieve Defense in Depth by Implementing Offensive Security Controls
Offensive security testing, such as penetration testing or external attack surface management, addresses the preventative side of a multi-layer defense in depth security program. Contrary to the popular view of offensive security, it’s not just about vulnerability discovery, but rather activities to help validate that the compensating controls are working as they’re intended to.
For example, if one control is bypassed, do you have a second layer of security to slow down the attacker? When issues are prevented in the first place, they have the potential for larger savings down the line, as opposed to when vulnerabilities are fixed after they become a problem or are exploited.
The steps to implement offensive security are simpler than you might think. With 88 percent of data breaches caused by human error, training staff to recognize phishing attempts is a great starting point. Shifting budget from cyber insurance premiums to offensive security measures puts organizations in a better position to prevent attacks and manage the cost of cyber insurance coverage.
Shifting budget from cyber insurance premiums to offensive security measures puts organizations in a better position to prevent attacks and manage the cost of cyber insurance coverage.
Offensive Security is for Everyone
At NetSPI, we’re seeing clients reinvest their cyber premium funds from reactive approaches to offensive security steps. As insurance costs continue to rise, it’s likely to become unbearable for organizations to continue paying these increasing amounts when they aren’t guaranteed a return on their investment.
This budget adds up over time, and security leaders may realize they could have added immense value to their overall security posture if they had shifted that spend to offensive security measures only a couple years ago. Cybersecurity leaders must begin shifting to offensive rather than reactive Cybersecurity programs today!
Let us help you make the shift! NetSPI’s offensive security consultants guide the steps toward a proactive security stance. Explore our full suite of penetration testing services.
Explore more blog posts
Hijacking Azure Machine Learning Notebooks (via Storage Accounts)
Abusing Storage Account Permissions to attack Azure Machine Learning notebooks
Celebrating NetSPI’s Partners of the Year 2024
Congratulations to NetSPI’s 2024 Partner of the Year Recipients Defy Security, VLCM, Softcat, Enduir, Evotek, and AWS

Exploiting Second Order SQL Injection with Stored Procedures
Learn how to detect and exploit second-order SQL injection vulnerabilities using Out-of-Band (OOB) techniques, including leveraging DNS requests for data extraction.